

The obtained knowledge is relevant for various experiments, such as industrial fermentation, prolonged experimental evolution or zero-growth studies, where sporulation is an undesirable trait that should be avoided, e.g by a sigF mutation.Ĭitation: Overkamp W, Kuipers OP (2015) Transcriptional Profile of Bacillus subtilis sigF-Mutant during Vegetative Growth. This is probably related to the arrest at sporulation stage II occurring in the sigF mutant, because continuation of growth from the formed disporic sporangia may require additional energy. The genes mildly down-regulated were mostly involved in anabolism and the genes mildly up-regulated, in particular fatty acid degradation genes, were mostly involved in catabolism.

The number of genes differentially expressed and the magnitude of expression were, as expected, quite small in comparison with sporulation conditions. Under these conditions that typically don’t induce sporulation, the transcriptome showed minor signs of sporulation initiation. Here, the impact of sigF disruption on the transcriptome of exponentially growing cultures is studied by micro-array analysis. The role of sigF is well studied under conditions that induce sporulation. Genetics, Bacillus subtilis, Gram-positive, spore formation, biological significance.Sigma factor F is the first forespore specific transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis and controls genes required for the early stages of prespore development. subtilis have been presented with emphasis on the basic genetic regulatory mechanisms. Furthermore, scientific advancements in the study of the spore formation process in B.
The molecular genetics, importance and industrial applications of these species as well as the historical perspective of Bacillus research have been reviewed.
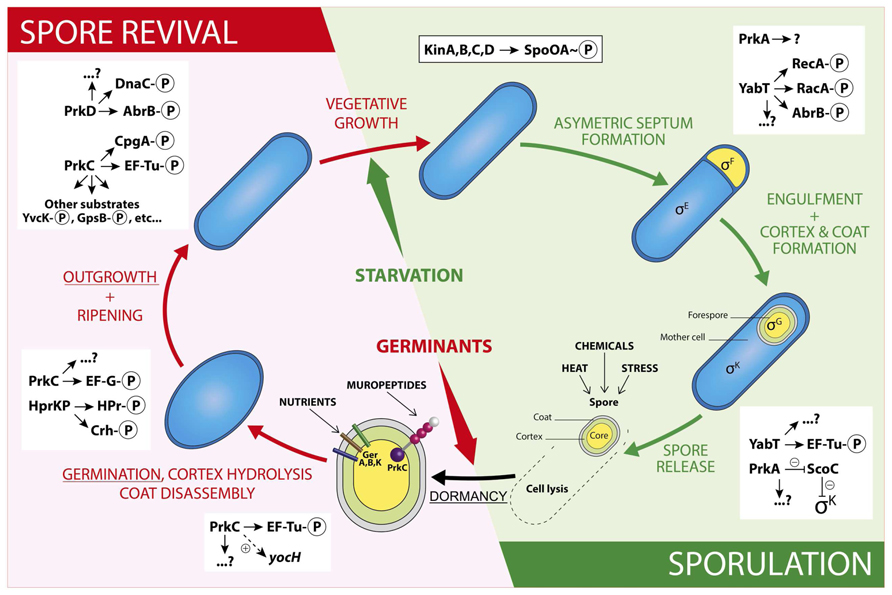
These processes eventually culminate in the formation of resistant spores. The process of spore formation involves cellular differentiation of an asymmetrically dividing mother cell, with each compartment undergoing distinct cell-specific gene expression. The bacteria survive adverse environmental conditions by undergoing a complex process of spore formation termed sporulation. Bacillus subtilis by virtue of its relatively simple cellular organization, experimental tractability and excellent genetics has become the principal paradigm for the study of the cellular processes of the Bacillus genus. Success in this regard depends on a thorough understanding of the species gene regulatory mechanisms, metabolism and secretary pathways. Optimization of the exploitation of these species has, therefore, become the major preoccupation of many laboratories worldwide. However, the immense potential for commercial scale production of these biomolecules still remain largely unexplored. *Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.īacillus species are important producers of essential biomolecules such as antibiotics, insecticides and enzymes. Box LG 80, Legon, Accra, Ghana and Department of Nuclear Agriculture and Radiation Processing, School of Nuclear and Allied Sciences, College of Basic and Applied Sciences, University of Ghana, Accra, Ghana. Biotechnology Centre, Biotechnology and Nuclear Agriculture Research Institute, Ghana Atomic Energy Commission, P.O.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
